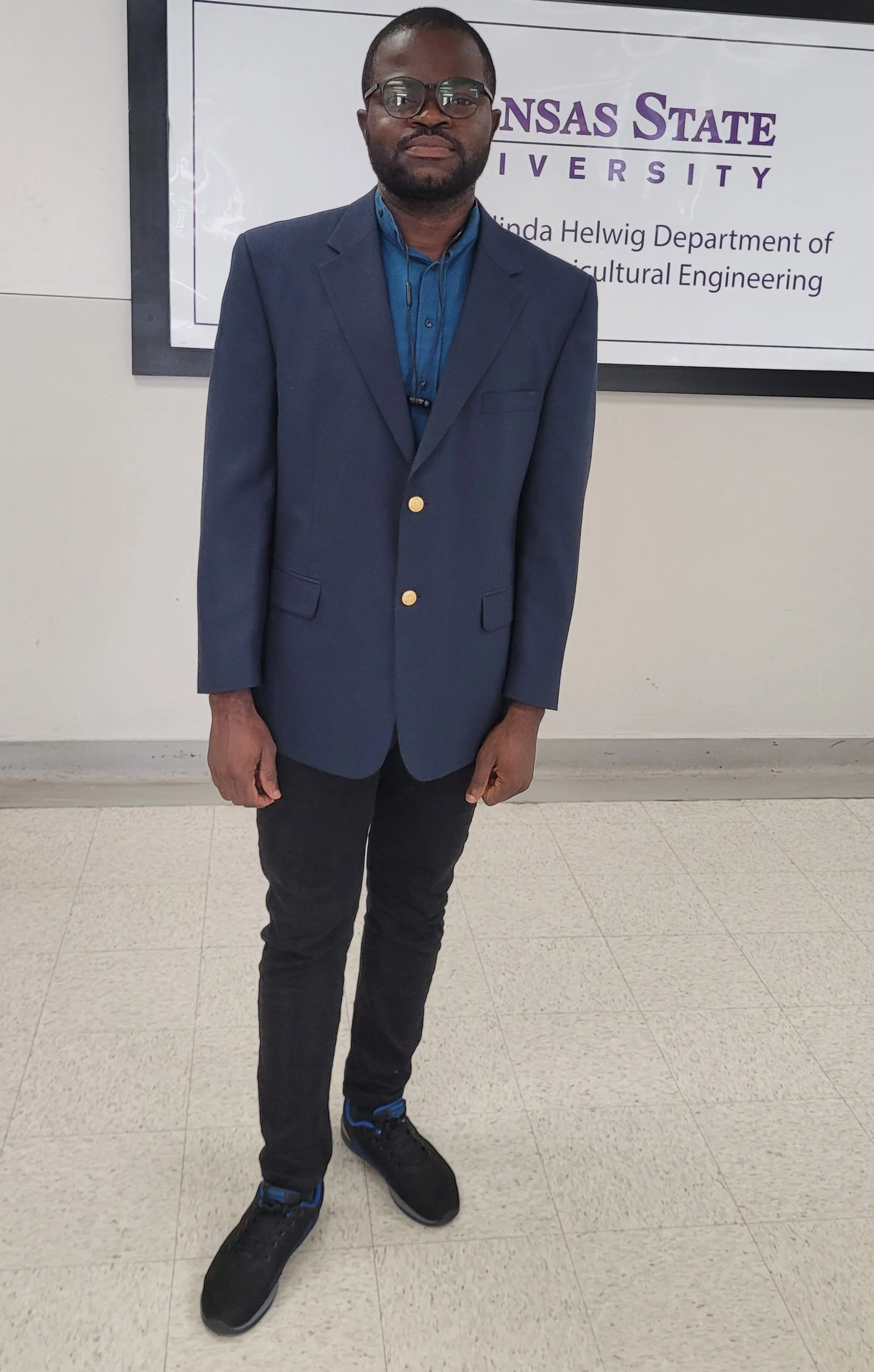
Two students awarded the Wayne Harrison Memorial Scholarship in 2024
The Wayne Harrison Memorial Scholarship supports academic and professional growth of students through funding research, management, or education projects related to wildland fire science. AFE received 8 strong applications for the scholarship this year, and a panel of four judges independently reviewed, scored the applications, and selected two awardees.
Congratulations to Bushra Sanira Asif and Izuchukwu Oscar Okafor!
Economic and Community Engagement Strategies for Wildfire Risk Mitigation
Bushra Sanira Asif, Doctoral Student
Risk, Climate Change and Sustainable Development University of Genoa, Italy
Awarded $2500
The integration of community stakeholders into wildfire risk management is crucial to combat increasing wildfire incidence and severity. This project investigates how economic tools and stakeholder engagement can collectively shape robust wildfire mitigation strategies. This funding will help create a participatory framework that incorporates stakeholder input into economic modeling of wildfire mitigation. The project goal is to merge financial and community-driven approaches to enhance the efficacy of wildfire management policies, ensuring they are both economically sound and socially responsive.
This project employs a mixed-methods approach that combines econometric analysis with qualitative research techniques. Econometric models will be developed to assess the financial impact of wildfires, while focus groups and interviews with a diverse array of stakeholders will provide insights into community-led mitigation efforts. It is important to first establish an economic baseline, then to enrich this with insights gained from stakeholder engagement, iteratively refining the model to ensure it is representative and actionable.
The project goal will be engaged through personal expertise in economics, growing knowledge of forestry management to mitigate fire impacts, and a proven track record of effective communication with diverse groups. With a commitment to a participatory approach, this project aims to foster a sense of shared ownership among stakeholders, which is critical for the successful adoption and implementation of wildfire risk mitigation strategies.
Adapting GFDI and KBDI for Safe and Smart Prescribed Burning in the Great Plains
Izuchukwu Oscar Okafor, Graduate Student
Biological and agricultural engineering Kansas State Unversity
Awarded $2500
Ranchers and farmers have long applied prescribed fires in the Great Plains of the United States, an area predominately grasslands, as an ecological management tool. Conducting prescribed burning at the right time within appropriate fire weather conditions ranges is critical for fire safety and offers the most practical way to reduce fire incidents and smoke impact. Increasing perceived risks associated with prescribed fire has reduced fire use in fire-adapted ecosystems within the Great Plains.
Unfortunately, current prescribed burning practices are largely traditional experience-based, constraining burning windows to fewer days annually. To restore trust in fire application in the region for ecological management, my research focuses on integrating the historical experience-based approach and data-driven statistical methods to unpack the benefits of prescribed fire use in the area. I acknowledge that responsible fire management relies on modelling tools that quantify fire-associated risks and environmental impact on air quality, hence my drive for the fire ecology thematic domain. The objectives of the project are to quantify prescribed fire risk levels for fine fuels, define optimal prescribed burn conditions for different burn objectives, quantify fire risks associated with prescribed burning and adapt Australia’s Grassland Fire Danger Indices (GFDI) and Keetch Byram Danger Indices after calibration with regional data as a step in expanding the narrowing burn window.